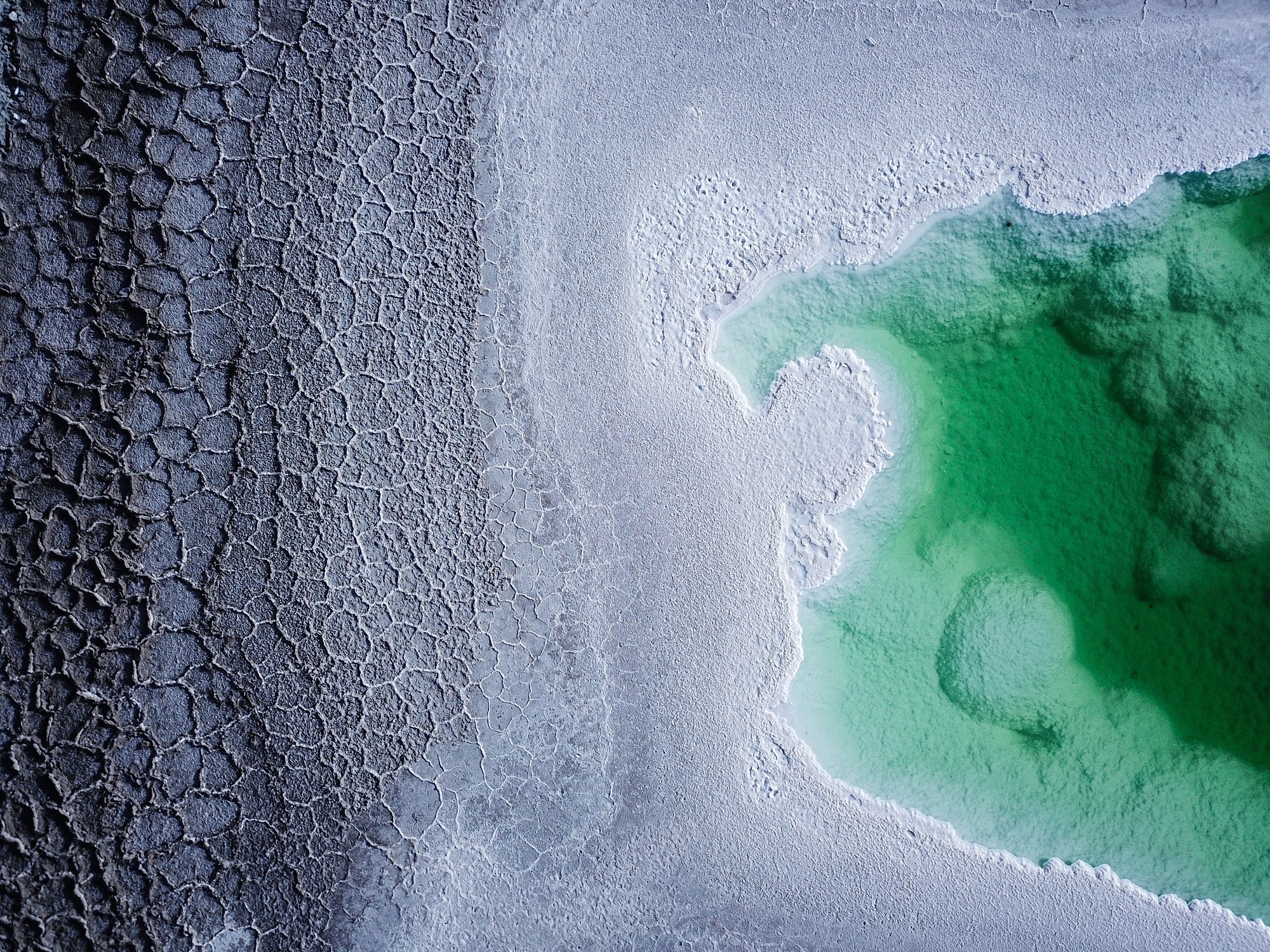
Sustainable development is a concept defined as the development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs by the World Commission on Environment and Development.
Sustainable development is clearly one of the most difficult challenges that humanity has ever faced. Attaining sustainability requires addressing many fundamental issues at local, regional, and global levels, and achieving the goals and objectives of sustainability presents a great challenge for all segments of society. A core principle of sustainable development is to improve human well-being and to sustain these improvements over time, but the consequences of climate change and the growing demand for energy and resources are making this objective more challenging.
Textile industries are one of the oldest models of industries which refer to those industries that are involved with the design, manufacturing, and distribution of cloths, dresses, and related goods. The textile manufacturing chain starts on a raw material basis controlled by agricultural subsidies and trade agreements, goes on through a chain of quick-reacting, market-driven processes, and ends up at a customer and consumer who is manipulated by the branding of wholesalers and the discount offer by retailers. This path is significant not only for economic behaviour of the textile markets, but also for the ecological aspects of textile production and consumption. Though textile industry is one of the major chemical industries, it is necessary to understand the waste generation and waste minimization-related procedures of the textile industries in-depth, alongside the waste generation and minimization-related procedures of chemical industries. Despite different initiatives of managing such waste, textile industry produced waste is yet one of the most hazardous groups of industrial waste.
Conceptually Cleaner Production seeks to integrate the continuous utilization of deterrent environmental approaches to processes, products and services aiming to rise efficiency and to minimize the risks to people and environment. The adoption of Cleaner Production practices collaborates to the preservation of raw materials and power, assures reduction or elimination of toxic materials and minimize the quantity of and the toxicity of the emissions and the residues during the production processes, and the textile, clothing and leather industries are priority for this Cleaner Production implementation.
Cleaner Production is propagated as an approach to identify preventive measures to reduce residues and emissions from the industrial activities applied in the textile industry by means of replacement of certain synthetic substances with natural materials especially those which are industrial by products organic natural materials can also be used, such as bamboo fibres; natural dyes to provide more ecological processes in dyeing and finishing of fabrics; or even replacement of toxic chemical products by less polluting ones.
Furthermore, the adoption of Cleaner Production in the textile industry is not limited to the development of new alternative materials, but there is space for technical improvement as well; innovation of cluster process management; investment in acquisition of new equipment with payback estimated in months and the adoption of life cycle assessment. The implementation of Cleaner Production can also be enforced by means of improvements in manufacturing processes, which enable the use of residual heat generated, increasing the energetic efficiency with the purpose to reduce energy consumption. Also, Cleaner Production can be achieved by the reduction of sodium chloride in the residual waters and the minimization of greenhouse effect gases. It is even possible to focus on the reduction of the volume of water to be disposed, aiming to reduce water consumption and disposal of water to the environment.
Can we say Cleaner Production in the textile industry, contribute to the Sustainable Development Goals?